In recent years, the automotive landscape has undergone a profound transformation, characterized by an unprecedented rise in the popularity of electric vehicles (EVs). As consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and environmental consciousness, automakers are responding with a diverse array of electric models, spurred on by advancements in technology, government incentives, and growing infrastructure support. This surge reflects not only a shift in consumer preferences but also a broader societal movement towards cleaner, more efficient means of transportation. In this article, we explore the factors driving this change, examine market trends, and consider the implications for the future of mobility as we transition into an era defined by electric driving.
Table of Contents
- Electric Vehicle Market Trends: Factors Driving Increased Adoption
- Environmental Impact: Assessing the Sustainability Benefits of Electric Cars
- Infrastructure Development: Preparing for the Future of Electric Transportation
- Consumer Insights: Addressing Concerns and Shaping Future Preferences
- Insights and Conclusions
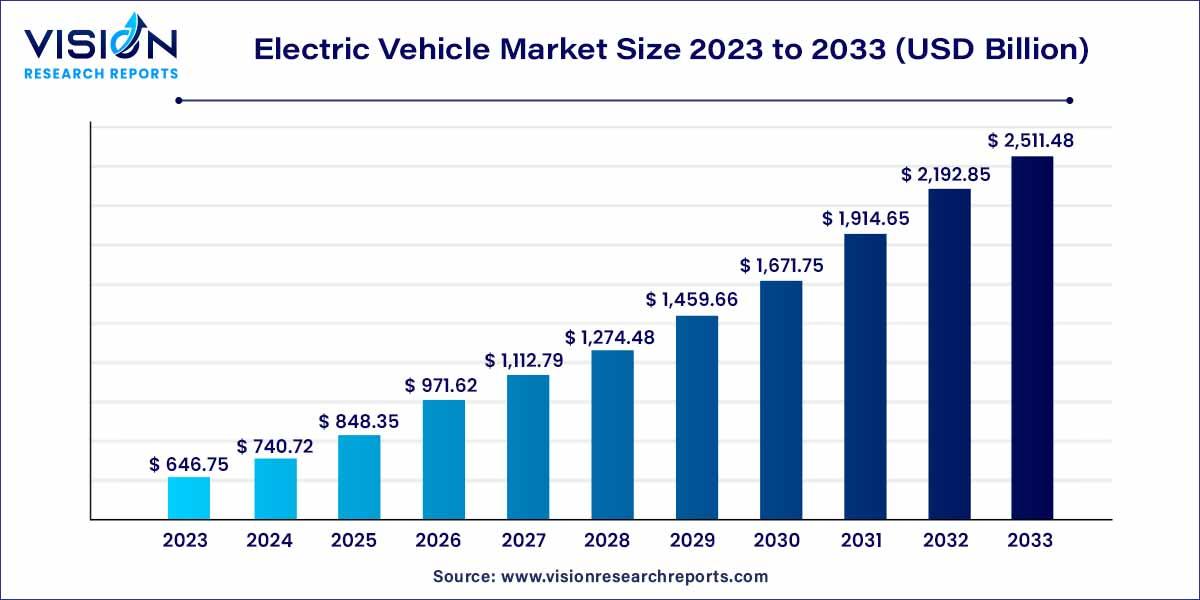
Electric Vehicle Market Trends: Factors Driving Increased Adoption
The surge in electric vehicle (EV) adoption is being driven by a confluence of several key factors that are reshaping the automotive landscape. One significant element is the rapid advancements in battery technology, which have led to improvements in range and accessibility. This progress not only alleviates consumer concerns regarding charging frequency but also contributes to a decrease in overall vehicle costs. Moreover, as major manufacturers commit to electrifying their fleets, the variety of models available has broadened, catering to a diverse array of consumer preferences and needs.
In addition to technological advancements, the role of government policies cannot be overlooked. Supportive regulations and financial incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, have been instituted in numerous regions to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles. These initiatives are complemented by an expanding network of charging infrastructure, making it more convenient for users to switch from traditional combustion engines to sustainable alternatives. The combination of these factors has created an environment ripe for growth in the EV market, reflecting a notable shift in consumer mindset towards sustainability and innovation.

Environmental Impact: Assessing the Sustainability Benefits of Electric Cars
The surge in electric car adoption is not just a passing trend; it is a pivotal moment in redefining our approach to sustainable transportation. As cities grapple with pollution, traffic congestion, and climate change, electric vehicles (EVs) are proving to be a compelling solution. They offer significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions when compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. Moreover, with advancements in battery technology and renewable energy sources, the carbon footprint associated with electric cars continues to diminish. Key benefits include:
- Reduced Air Pollution: EVs operate with zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly improves urban air quality.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electric vehicles generally have lower maintenance costs and offer savings on fuel when charged with renewable energy.
- Energy Independence: Increased use of electric cars can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, promoting energy sustainability.
Moreover, the impact of widespread electric vehicle adoption extends beyond individual car owners. When integrated into mass transit systems, EVs can catalyze a broader shift towards sustainable urban mobility. The transition will not only be beneficial for the environment but also economically viable as evidenced by recent trends showing declining manufacturing costs and increased consumer demand. To understand the tangible benefits of this technology, consider the following table showcasing the comparative emissions of electric vehicles versus traditional vehicles:
| Vehicle Type | Average CO2 Emissions (g/km) |
|---|---|
| Electric Vehicle | 0 |
| Gasoline Vehicle | 130 |
| Hybrid Vehicle | 90 |
Infrastructure Development: Preparing for the Future of Electric Transportation
The rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates a robust and expansive network of charging infrastructure that can keep pace with the rapid transition to electric transportation. Municipalities and private sectors are partnering to deploy charging stations across urban and rural locations, aiming to create a seamless driving experience for EV owners. This transformation not only addresses range anxiety—one of the primary concerns for potential EV buyers—but also supports the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. Key components of this development include:
- Fast Charging Stations: Essential for reducing downtime and enhancing convenience, especially along major highways.
- Home Charging Solutions: Encouraging the installation of domestic charging units to facilitate overnight recharging.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating consumers about the availability and benefits of charging networks.
In addition, innovative technological advancements are paving the way for smarter infrastructure that can dynamically adapt to the growing needs of electric transportation. Smart charging systems can optimize energy usage based on grid demands and peak hours, while solar-integrated charging stations are emerging as a sustainable solution. To better understand the landscape of current infrastructure development, consider the table below showcasing the expansion of charging stations in key regions:
| Region | Charging Stations (2022) | Projected Growth (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 25,000 | 75,000 |
| Europe | 80,000 | 200,000 |
| Asia-Pacific | 50,000 | 150,000 |
Consumer Insights: Addressing Concerns and Shaping Future Preferences
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) is accompanied by a shift in consumer priorities, leading manufacturers to address various concerns voiced by potential buyers. Key insights into consumer behavior reveal that environmental awareness is driving the demand for sustainable transportation options. However, concerns about charging infrastructure, battery life, and initial costs remain significant barriers. Consumers are particularly interested in:
- Charging Accessibility: Easy access to charging stations is essential for EV adoption.
- Pricing Transparency: Clear comparison between EVs and traditional vehicles can enhance consumer confidence.
- Battery Technology: Advances in battery life and efficiency are crucial for meeting consumer expectations.
Survey data indicate that nearly 70% of consumers are willing to consider electric cars if these concerns are adequately addressed. As manufacturers innovate and collaborate with tech companies to enhance the consumer experience, their focus should also extend to educating buyers on the long-term economic benefits of EVs. The following table outlines consumer preferences that may shape future market strategies:
| Consumer Concern | Priority Level | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Infrastructure | High | Expansion of Fast-Charging Stations |
| Cost of Ownership | Medium | Incentives and Rebates |
| Reliability of Technology | High | Improved Battery Lifespan |
Insights and Conclusions
the remarkable surge in the popularity of electric cars marks a significant shift in the transportation landscape, driven by advancements in technology, growing environmental awareness, and supportive government policies. As consumers increasingly opt for sustainable alternatives, automakers are responding with an expanding range of electric vehicle options, aimed at meeting diverse needs and preferences. This transition not only aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change but also signifies a pivotal moment in the evolution of personal and public transportation. As we move forward, the continued investment in charging infrastructure and technological innovation will be crucial in supporting this momentum. The future of transportation is indeed electric, and its implications will resonate across economic, social, and environmental dimensions for years to come.