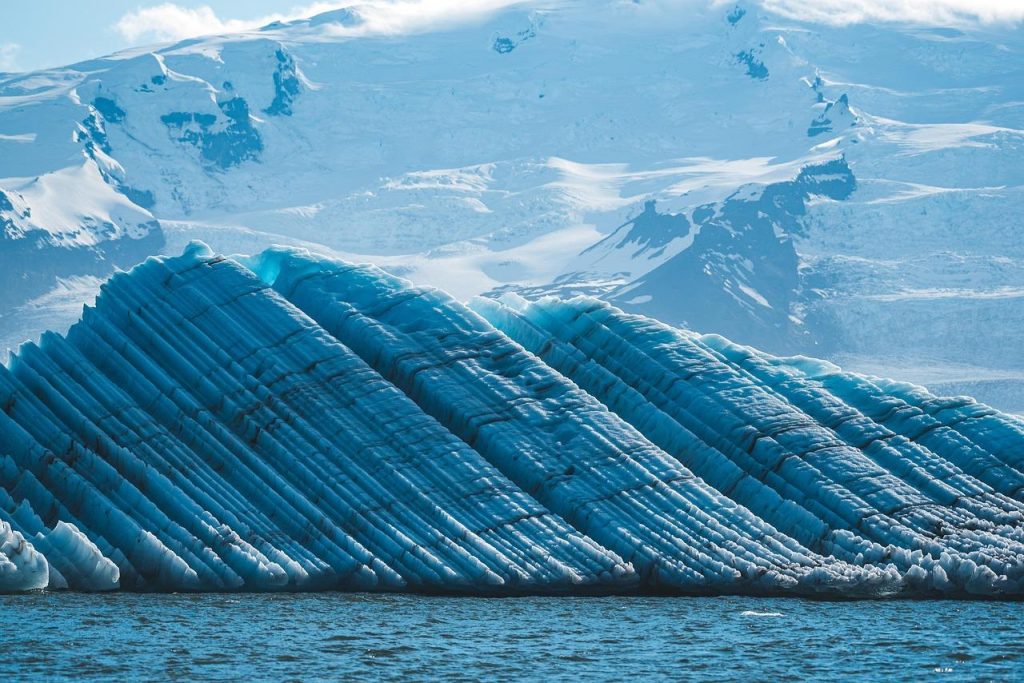
In the grand tapestry of Earth’s history, glaciers stand as silent sculptors, wielding their icy tools to carve the landscape into magnificent forms. These ancient rivers of ice, born from the compression of snow over millennia, embody a paradox: both gentle and fierce, they have the power to alter mountains and shape valleys with an artistry that speaks to the slow, relentless march of time. As they advance and retreat, glaciers not only reshape the physical world around them but also influence ecosystems, climates, and even human civilizations. This article explores the transformative power of glaciers, revealing how their relentless presence has forged the Earth’s contours, sculpted its beauty, and left an indelible mark on the natural world. Through a journey into the heart of these frozen giants, we will uncover the secrets they hold and the profound impacts they continue to exert on our planet.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Glacier Dynamics and Their Role in Shaping Landscapes
- The Impact of Glacial Melt on Ecosystems and Sea Levels
- Harnessing Glacial Energy: Sustainable Solutions for the Future
- Preserving Glacier Heritage: Strategies for Conservation and Research
- Wrapping Up
Understanding Glacier Dynamics and Their Role in Shaping Landscapes
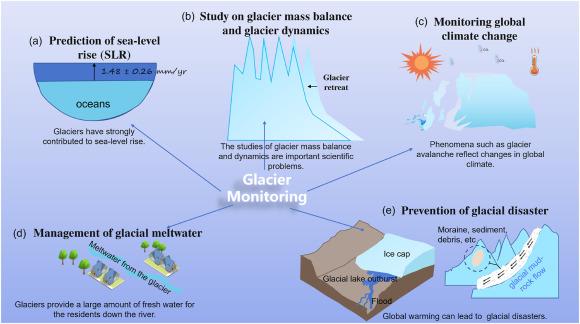
Glaciers are nature’s slow but powerful sculptors, playing an essential role in shaping our planet’s landscapes over millennia. As they advance and retreat, they gnaw at the earth beneath them, creating distinctive geological features. The process begins with accumulation of snow, which compacts into ice. This massive ice body then moves under its own weight, driven by gravity, resulting in various physical changes to the environment. Through
- Glacial Erosion: The scraping away of rock and soil, forming valleys, fjords, and sharp mountain peaks.
- Transport of Sediments: Glaciers carry debris and sediment, redistributing materials across vast distances.
- Deposition: When glaciers melt, they release sand, gravel, and boulders, creating landforms like moraines and outwash plains.
The intricate interplay of these processes not only alters topography but also influences ecosystems and human activities. Some regions see glacial lakes forming in depressions left by receding glaciers, while others experience the creation of fertile plains ideal for agriculture. Additionally, these icy giants have significant implications for water resources, as they feed rivers and replenish aquifers upon melting. The rhythmic ebb and flow of glaciers thus serves as a stark reminder of nature’s power and the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems.
| Glacial Features | Formation Process |
|---|---|
| U-shaped valleys | Erosion by advancing glaciers |
| Hanging valleys | Subsequent erosion of tributary glaciers |
| Cirques | Carving by ice at high altitudes |
| Moraines | Deposition of debris |
The Impact of Glacial Melt on Ecosystems and Sea Levels
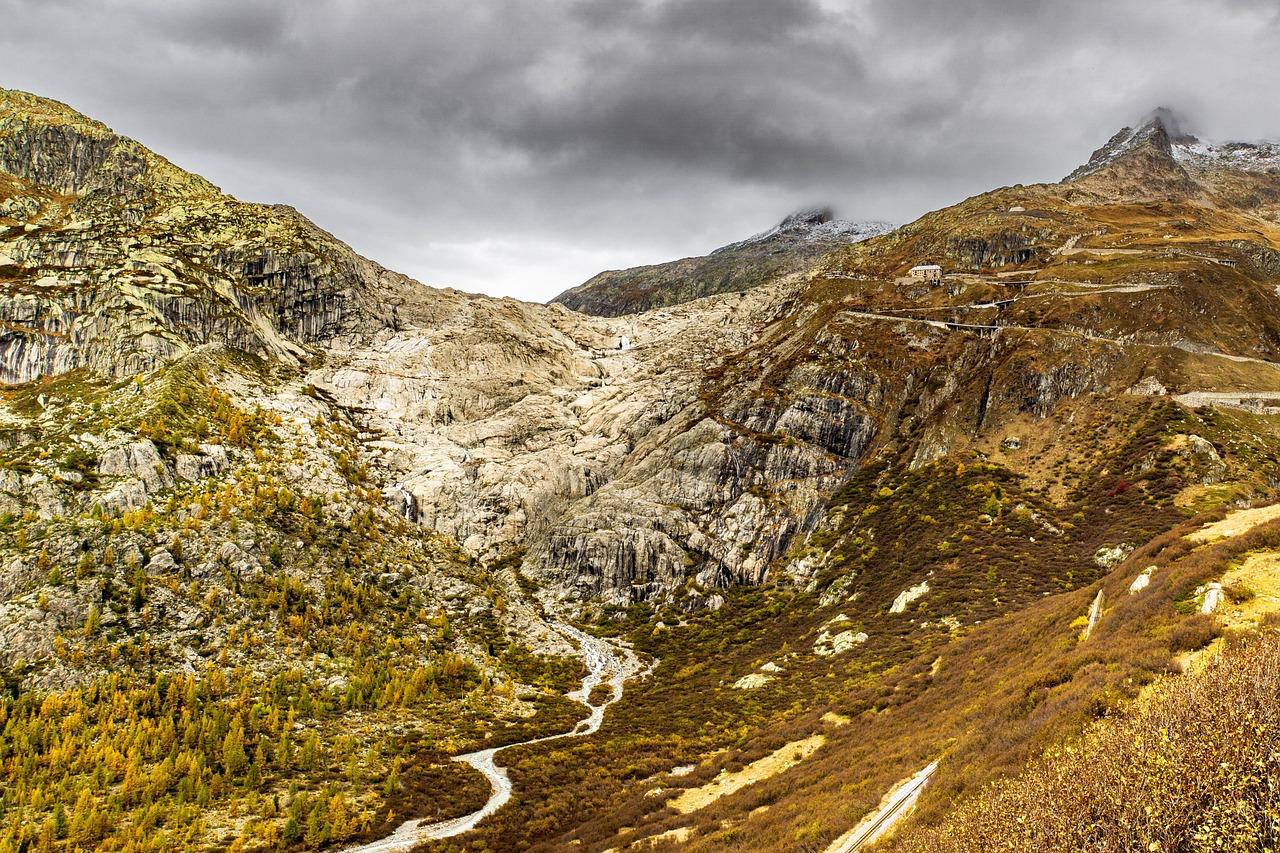

The terrestrial realm feels the profound consequences of glacial melt, casting ripples through our ecosystems. As vast glaciers recede, they release freshwater into the oceans, altering salinity and affecting marine life. This influx leads to changes in nutrient cycles, which can disrupt established food webs, potentially threatening endangered species and altering population dynamics. Additionally, glacial melt exposes land that was once frozen for millennia, which can introduce new plant species and shift existing flora’s distribution, thereby revitalizing and reshaping terrestrial ecosystems.
Moreover, the rise in sea levels—an inevitable outcome of melted glaciers—poses threats to coastal habitats and human settlements. Current projections indicate a significant rise in sea levels over the next century, leading to a variety of dire outcomes, such as:
- Coastal Erosion: Increased flooding and erosion of shorelines, compromising habitats.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Contamination of freshwater aquifers affecting agriculture and drinking water.
- Population Displacement: Communities relocated due to inundated land, leading to environmental refugees.
| Impact | Details |
|---|---|
| Increased Habitat Loss | Destruction of coastal ecosystems like mangroves and wetlands. |
| Loss of Biodiversity | Species unable to adapt or migrate face extinction. |
| Economic Consequences | Rising costs for infrastructure and disaster management. |
Harnessing Glacial Energy: Sustainable Solutions for the Future
Glaciers, the slow-moving giants of ice, have long been recognized for their breathtaking beauty and formidable power, but they also hold untapped potential as a sustainable energy source. As climate change accelerates glacial melt, harnessing the energy produced from melting glaciers could revolutionize our approach to renewable resources. By utilizing advanced technologies, we can transform this natural phenomenon into a consistent and clean energy supply. This shift not only provides an alternative to fossil fuels but also minimizes the overall impact on surrounding ecosystems. Through innovative projects, communities in glacial regions can transition towards energy independence, using a resource that has shaped our landscapes for millennia.
Among the strategies for harnessing glacial energy are methods such as hydropower generation, thermal energy conversion, and sustainable tourism. Each method presents unique opportunities to blend ecological awareness with energy production. For instance, leveraging the flow of glacial meltwater can power turbines in hydropower stations, providing local grids with a steady output. Additionally, thermal energy systems can capture the heat difference between melting ice and the surrounding environment, generating electricity while minimizing waste. As societies look for integrated approaches, investing in glacial energy, can serve as a pivotal step towards a more sustainable future.
- Hydropower: Utilizing glacial meltwater flow to produce clean energy.
- Thermal Energy: Converting temperature differentials for electricity generation.
- Sustainable Tourism: Creating eco-friendly tourist experiences that support local economies and education on glacial systems.
| Energy Source | Method of Harnessing | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hydropower | Turbine systems using meltwater flow | Reliable electricity generation |
| Thermal Energy | Heat capture from glacial activity | Reduced carbon footprint |
| Sustainable Tourism | Eco-guided tours and education | Local economic growth and conservation awareness |
Preserving Glacier Heritage: Strategies for Conservation and Research
As glaciers retreat at an alarming rate, the heritage they embody is at risk, necessitating innovative strategies for both conservation and research. Collaborative initiatives between governments, environmental organizations, and academic institutions can enhance our understanding of glacial dynamics. Through methods such as field studies, satellite monitoring, and community engagement, we can gather critical data to inform conservation efforts. Education and awareness are equally vital; fostering a public understanding of glacier ecosystems encourages stewardship that transcends borders. Additionally, integrating traditional ecological knowledge from indigenous populations can provide unique insights into sustainable practices that have preserved these natural wonders for generations.
The implementation of dedicated conservation programs is essential for safeguarding these fragile landscapes. Some effective strategies include:
- Establishing protected areas to limit human impact
- Enhancing research funding focused on glacial science
- Developing climate action frameworks to mitigate global warming
- Promoting eco-tourism that supports conservation while providing economic benefits to local communities
Furthermore, investments in technology can revolutionize our approach to glacier conservation. Utilizing tools such as drones, GIS mapping, and climate modeling enables researchers to monitor changes with unprecedented precision. A recent study highlighted these advancements:
| Technology | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Drones | Mapping glacier morphology | Cost-effective and high-resolution imagery |
| GIS Mapping | Tracking glacial retreat | Integrates data for comprehensive analysis |
| Climate Models | Forecasting future conditions | Informs policy and conservation strategies |
By committing to these multifaceted approaches, we not only preserve glacier heritage but also enhance our understanding of the broader environmental shifts impacting our planet.
Wrapping Up
As we conclude our exploration of glaciers and their extraordinary influence on the Earth’s landscape, we are reminded of the intricate dance between nature’s forces and the land beneath our feet. These colossal ice masses, though seemingly static, hold within them a dynamic story of transformation—sculpting valleys, nurturing ecosystems, and shaping our climate.
Each crevasse and ridge is a testament to the patience of time and the relentless power of nature. As we observe the gradual carving of our planet, it serves as a poignant reminder of the delicate balance that sustains our environment. In an age where climate change looms heavily, understanding the role of glaciers can illuminate our responsibility as stewards of the Earth.
As we move forward, let us carry with us the lessons etched in ice; that change is inevitable, resilience is essential, and our actions today will echo through the canyons of tomorrow. May we strive to harmonize our existence with the powerful forces that shape our world, ensuring that the beauty and majesty of glaciers remain, not just as relics of the past, but as vital threads in the ongoing tapestry of our planet’s story.