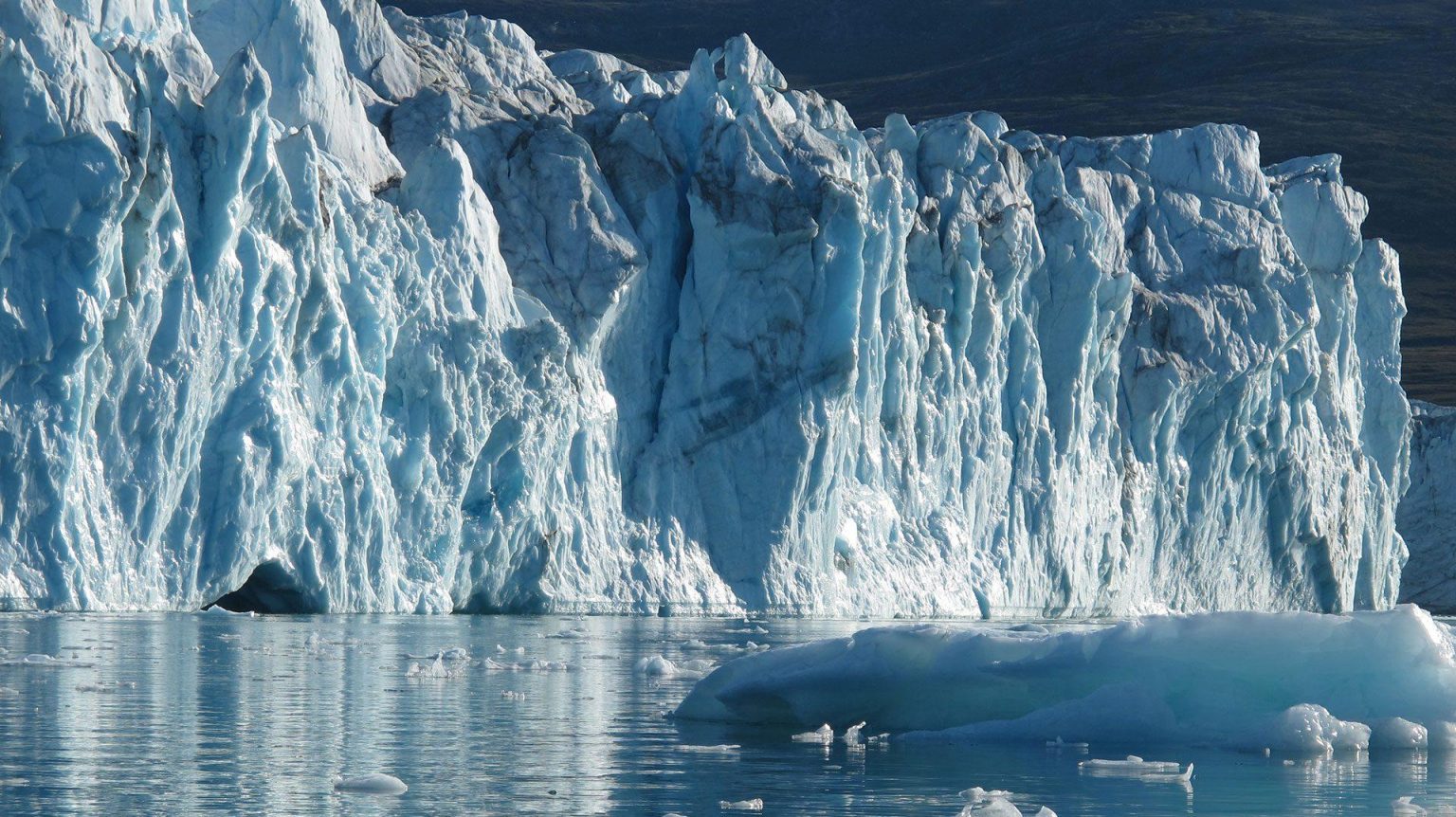
Beneath the icy surface of our planet lies a story of transformation, one written in the language of ice and time. Glaciers, those immense rivers of ice that seem to move with an otherworldly grace, play an extraordinary role in sculpting the Earth’s landscape. From the soaring peaks of the Himalayas to the deep valleys of North America, their relentless advance and retreat shape not just the physical world, but also the ecosystems and climates we inhabit. As silent architects of the wilderness, glaciers wield a power that is both subtle and profound, sculpting mountains, carving valleys, and whispering secrets of our planet’s past. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate dynamics of glaciers, their immeasurable influence on geography, and the critical lessons they impart about climate change, reminding us that even the mightiest forces of nature can be vulnerable. Join us as we uncover the remarkable ways in which these frozen titans continue to shape the Earth beneath our feet.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Glacial Dynamics and Their Impact on Landscapes
- The Role of Glaciers in Shaping Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- Mitigating Climate Change: The Future of Glacial Regions
- Embracing Sustainable Practices for Glacial Preservation
- To Conclude
Understanding Glacial Dynamics and Their Impact on Landscapes
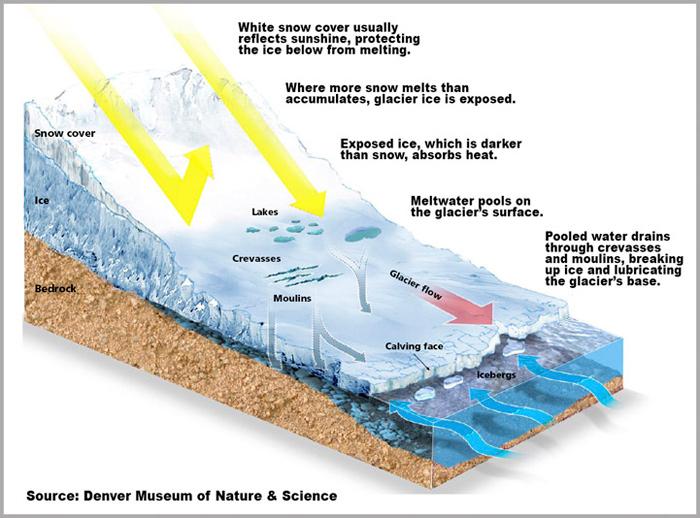
Glaciers are dynamic systems that continuously reshape the Earth’s surface through their movement and the forces they exert. As they advance or retreat, these massive rivers of ice carve out valleys and create distinct landforms. This process of erosion is powerful, and it manifests in various geological features such as U-shaped valleys, moraines, and fjords. The sheer weight of the ice compresses the underlying bedrock, allowing the glacier to grind down the surface as it moves. Over millennia, this relentless action has transformed rugged terrains into breathtaking landscapes, illustrating nature’s ability to sculpt the environment.
Moreover, the impact of glacial dynamics extends beyond mere physical alterations; it also influences local ecosystems and hydrology. As glaciers melt, they release freshwater into rivers and lakes, which can lead to an increase in biodiversity in the surrounding areas. This glacial meltwater is crucial for maintaining water supplies, particularly in regions where seasonal snow and ice serve as a lifeline. The connections between glaciers and their environments highlight a delicate balance, as changing climate conditions threaten these icy giants. The following table illustrates the essential features affected by glacial movements:
| Feature | Impact of Glaciers |
|---|---|
| U-shaped Valleys | Formed by glacial erosion, creating broad, flat floors. |
| Moraines | Accumulations of debris that mark glacier movement. |
| Fjords | Deep, narrow inlets created by glacial carving. |
| Meltwater Lakes | Vital freshwater sources that support local ecosystems. |
The Role of Glaciers in Shaping Ecosystems and Biodiversity
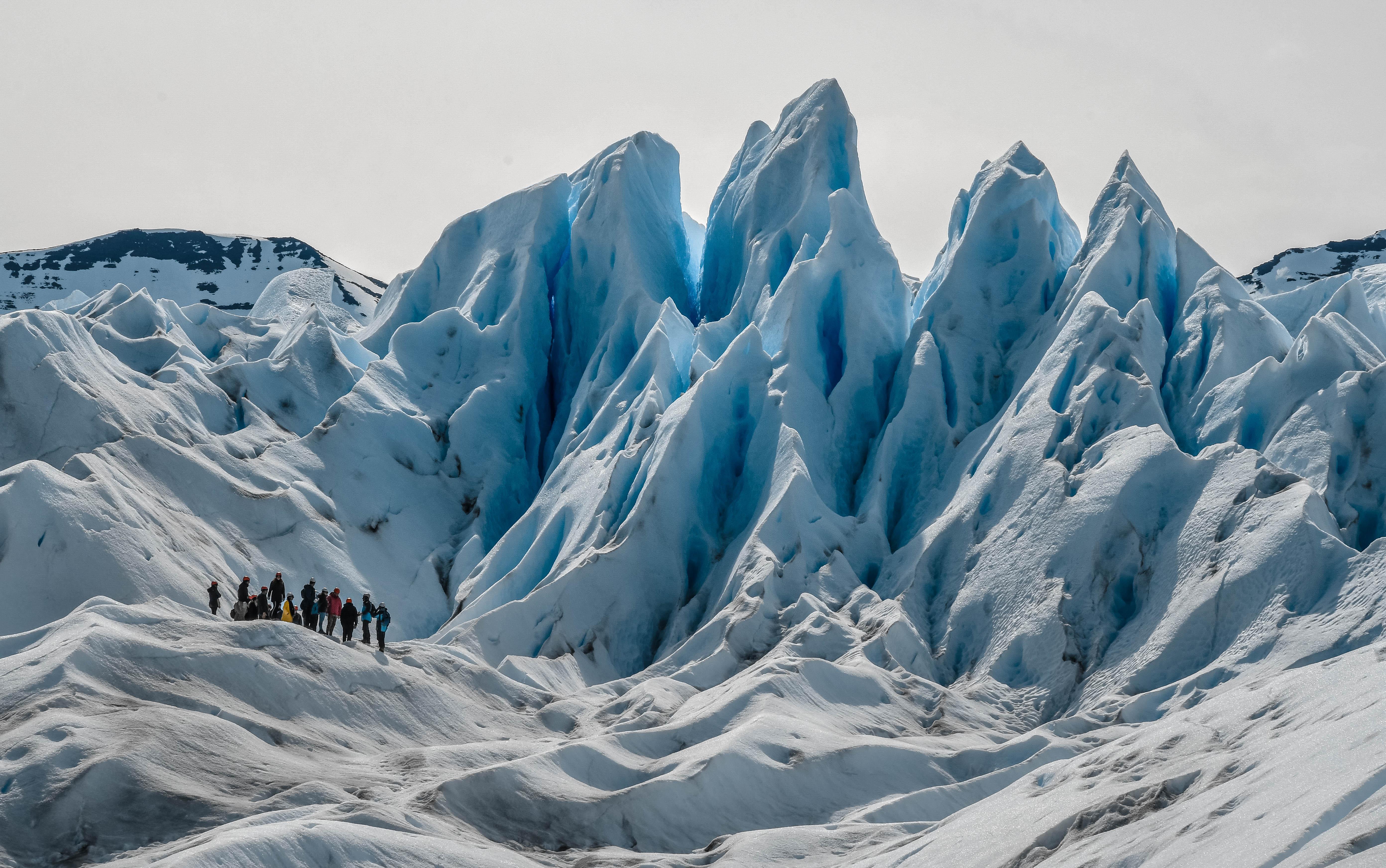

Glaciers are not merely slow-moving rivers of ice; they are dynamic agents of change that sculpt the landscape and pave the way for diverse ecosystems to flourish. As glaciers advance and retreat, they carve out valleys, shape mountains, and create various landforms that influence local climates. These changes in the environment lay the groundwork for an array of habitats. As the ice melts, it exposes bare rock and soil, which serve as a foundation for new plant life. Over time, pioneer species establish themselves, providing food and shelter for other organisms. This sequence of ecological succession is vital in building a robust ecosystem, promoting biodiversity that thrives in the shadow of glacial formations.
Moreover, the hydrology of glacial regions is instrumental in sustaining ecosystems. Meltwater from glaciers feeds rivers, lakes, and wetlands, creating habitats rich in biodiversity. This water plays a critical role in various biological processes, facilitating the migration of species and supporting flora and fauna that depend on freshwater sources. The unique conditions fostered by glacial landscapes also contribute to the phenomenon of glacial refugia, where species can survive climatic changes and maintain genetic diversity. Important aspects include the following:
- Habitats for unique species: Glacial regions often harbor endemic species that have adapted specifically to these harsh environments.
- Water source for ecosystems: Meltwater is essential for sustaining plant life and supporting animal populations.
- Influence on weather patterns: The presence of large ice masses can modify local climates, impacting precipitation and temperature.
Mitigating Climate Change: The Future of Glacial Regions
As the planet warms, glacial regions are becoming critical barometers of climate health. The shrinking of glaciers not only symbolizes the stark realities of climate change but also highlights the dire consequences for ecosystems and communities dependent on glacial meltwater. To mitigate these effects, innovative strategies are essential. This includes:
- Restoration Projects: Efforts to restore neighboring ecosystems can enhance biodiversity.
- Water Management Policies: Developing sustainable water management practices to optimize the use of glacial meltwater.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Investing in renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, local communities play a vital role in the preservation of glacial environments. Engaging with indigenous knowledge can provide insights into sustainable practices and adaptation strategies that have stood the test of time. An accessible overview of local initiatives could include:
| Community Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Glacier Monitoring Programs | Involving locals in tracking changes in glacier size and composition. |
| Ecosystem Restoration Workshops | Educating communities on restoring native flora and fauna affected by glacial retreat. |
| Renewable Energy Co-ops | Collaborative projects to harness local renewable resources, reducing carbon footprints. |
Embracing Sustainable Practices for Glacial Preservation
As the world observes the alarming signs of climate change, the responsibility to safeguard our glaciers has never been more pressing. By embracing sustainable practices, we can significantly mitigate the impact of human activity on these majestic ice formations. This includes prioritizing renewable energy sources, reducing carbon footprints, and promoting eco-friendly tourism that respects glacial ecosystems. Some effective strategies include:
- Implementing waste reduction initiatives: Encouraging recycling and proper waste disposal in glacial regions.
- Creating awareness programs: Educating travelers about the importance of glacier preservation and how to minimize their impact.
- Advocating for local legislation: Supporting policies that protect natural resources and manage climate change on a local level.
Sustainable practices not only help in the preservation of glaciers but also foster a deeper connection between humanity and nature. Collaborative efforts among governments, organizations, and local communities can lead to innovative solutions to preserve these natural wonders. Consider the following key initiatives:
| Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reforestation programs | Enhance local ecosystems and absorb CO2. |
| Eco-tourism certifications | Promote responsible travel practices. |
| Research collaborations | Advance scientific understanding of glacial dynamics. |
To Conclude
As we conclude our exploration of “,” it becomes clear that these ancient giants are far more than just blocks of ice. They are dynamic architects of our planet, shaping landscapes and ecosystems with both grace and ferocity. From the towering peaks of the Himalayas to the serene valleys of the Swiss Alps, glaciers continue to carve their stories into the Earth, leaving behind a legacy that speaks to the intricate dance between climate and geography.
Understanding glaciers is not merely an exercise in observing the past; it is also a contemplation of our future. As temperatures rise and ice retreats, the impact of these glaciers will be felt in every corner of the globe, influencing sea levels, weather patterns, and the very ecosystems that rely on their existence.
In this ongoing saga of nature’s artistry, we are called to respect these mighty forces and advocate for their preservation. Glaciers remind us of the delicate balance of our environment and the profound effects of time and change. As we reflect on their role in sculpting the land beneath our feet, let us also remember our responsibility to protect these frozen sentinels, ensuring that they continue to tell their story to generations yet to come.