In the heart of bustling cities and secluded natural landscapes alike, zoos stand as intricate tapestries interwoven with the threads of education, conservation, and the preservation of biodiversity. While their primary allure may often lie in the wonder of witnessing exotic wildlife up close, the role of these institutions extends far beyond mere entertainment. As the global crisis of species extinction escalates, raising alarming concerns about our planet’s future, zoos are increasingly stepping into the spotlight, offering insights into their profound impact on animal conservation efforts. This journey into the world of modern zoos reveals their evolving mission—one that seeks to bridge the gap between humanity and wildlife, fostering a deeper understanding of our shared responsibility for the earth’s inhabitants. We embark on an exploration of how these establishments contribute to global conservation initiatives, the challenges they face, and the innovative strategies they are employing to ensure that the roar of the lion and the call of the tropical bird continue to resonate through our world for generations to come.
Table of Contents
- The Role of Zoos in Protecting Endangered Species
- Evaluating the Educational Benefits of Zoos for Conservation Awareness
- Partnerships Between Zoos and Wildlife Organizations: A Collaborative Approach
- Recommendations for Enhancing Zoos Contribution to Global Conservation Efforts
- To Wrap It Up
The Role of Zoos in Protecting Endangered Species

Zoos have evolved beyond mere entertainment venues, emerging as pivotal actors in the global effort to protect endangered species. Through comprehensive breeding programs, they create genetic reservoirs that help prevent the extinction of vulnerable species in the wild. Many zoos participate in cooperative breeding initiatives, where they share knowledge and resources, maximally diversifying the gene pool. This collaboration not only aids in maintaining species populations but also prepares them for potential reintroduction into their natural habitats. Additionally, many zoos invest in conservation projects that address the root causes of endangerment, such as habitat loss and poaching, working directly with local communities to foster sustainable practices.
The educational role of zoos should not be underestimated; they provide a platform for visitors to learn about the plight of endangered species and the ecosystems they inhabit. By fostering empathy and awareness, zoos catalyze public support for conservation initiatives. Engaging programs, such as interactive exhibits and behind-the-scenes tours, allow guests to form connections with the animals, igniting a passion for wildlife conservation. Furthermore, many zoos allocate a portion of their funding to global conservation efforts, actively contributing to research, habitat restoration, and anti-poaching campaigns. The symbiotic relationship between zoos and conservation organizations enables a broader impact, helping to harness public interest into meaningful action for the future of our planet’s biodiversity.
| Conservation Initiatives | Description |
|---|---|
| Breeding Programs | Captive breeding to increase population numbers. |
| Habitat Restoration | Efforts to restore natural habitats for endangered species. |
| Research Funding | Financial support for conservation research and studies. |
| Community Engagement | Collaborating with local communities for sustainable practices. |
Evaluating the Educational Benefits of Zoos for Conservation Awareness
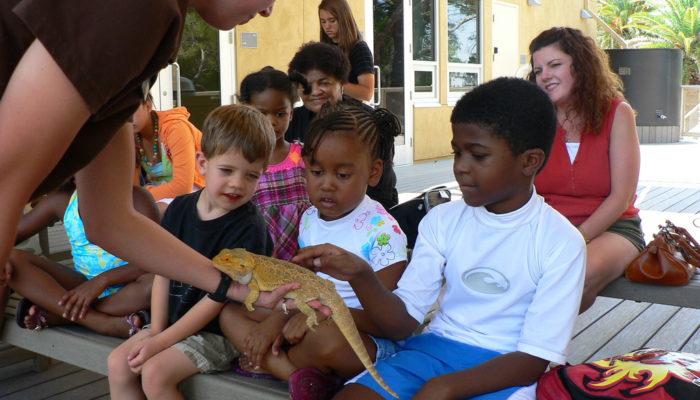

Zoos have increasingly become more than just mere displays of wild animals; they have evolved into pivotal centers for education and conservation awareness. Through interactive exhibits and informative programs, visitors are given the opportunity to engage with wildlife on a deeper level. Schools frequently organize field trips to zoos, where students can learn about the importance of biodiversity, ecosystems, and the role endangered species play in maintaining ecological balance. This firsthand experience fosters a sense of responsibility and connection to the natural world, essential for the cultivation of future conservationists. Key aspects of these educational benefits include:
- Hands-On Learning: Engaging with animals encourages curiosity and fosters a desire to learn.
- Awareness Campaigns: Many zoos run campaigns that target specific conservation issues, raising awareness among visitors.
- Workshops and Talks: Educational workshops held by conservationists and animal care professionals can provide deeper insights into wildlife challenges.
Furthermore, the educational initiatives spearheaded by zoos can result in measurable impacts on conservation awareness. Many zoos conduct post-visit surveys to assess changes in attitudes towards animals and conservation issues. These surveys often reveal that visitors are more likely to support wildlife preservation efforts after their experiences. A recent study compiled data on visitor responses:
| Indicator | Before Visit (%) | After Visit (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness of Endangered Species | 30 | 70 |
| Support for Conservation Efforts | 25 | 65 |
| Willingness to Volunteer | 15 | 40 |
This data highlights the potential of zoos to not only educate but also inspire action among individuals regarding conservation efforts. Educating the public is crucial to fostering a community that values and actively participates in preserving wildlife and natural habitats.
Partnerships Between Zoos and Wildlife Organizations: A Collaborative Approach
The collaboration between zoos and wildlife organizations has emerged as a vital strategy in the quest for global animal conservation. Through their combined resources and expertise, these partnerships effectively address pressing issues such as habitat destruction, poaching, and species extinction. Zoos contribute not just as exhibition spaces, but as active players in conservation efforts by:
- Conducting vital research on animal behavior and genetics.
- Implementing breeding programs for endangered species.
- Educating the public about conservation through engaging exhibits and programs.
Wildlife organizations, on the other hand, provide critical support in the form of fieldwork and conservation strategies, often in locations where animals are facing immediate threats. Together, they develop and execute multi-faceted programs that create a sustainable impact on wildlife populations around the globe.
Such partnerships often lead to the establishment of educational initiatives that raise awareness of the conservation challenges species face. These programs not only promote understanding among zoo visitors but also inspire action. The effectiveness of these collaborations can be exemplified through successful projects, such as:
| Project Name | Focus Area | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Species Survival Plan | Biodiversity Preservation | Increased population of captive-bred species |
| Wildlife Rescue Operations | Anti-Poaching | Rehabilitation of injured wildlife |
| Conservation Education Outreach | Public Awareness | Enhanced community participation in local conservation efforts |
These examples illustrate the success achievable when zoos and wildlife organizations unite their strengths in the face of escalating ecological challenges.
Recommendations for Enhancing Zoos Contribution to Global Conservation Efforts
To amplify their role in global conservation, zoos should consider implementing a multifaceted strategy that emphasizes education, research, and collaboration. Educational programs can serve as a cornerstone for raising public awareness about endangered species and the challenges they face in their natural habitats. By designing engaging workshops and interactive exhibits, zoos can inspire visitors to become active participants in conservation efforts. Additionally, prioritizing wildlife research not only advances scientific knowledge but also aids in developing effective conservation strategies that can be shared with other organizations and governments. Collaboration between zoos, NGOs, and governmental bodies will ensure a unified approach, maximizing resource utilization and enhancing the overall impact of conservation initiatives.
Moreover, fostering community engagement is crucial for creating lasting relationships between local populations and wildlife conservation efforts. Zoos can establish local programs that empower communities to participate in conservation activities, such as habitat restoration or species monitoring. This not only strengthens the bond between humans and nature but also provides vital data for conservationists. Furthermore, integrating technological advancements, such as virtual reality experiences or mobile conservation apps, can broaden the reach and effectiveness of conservation messaging. By adopting these approaches, zoos can position themselves as vital players in global conservation efforts, uniting knowledge with action to protect our planet’s biodiversity.
To Wrap It Up
As we reflect on the intricate tapestry of global animal conservation, it becomes clear that zoos play a multifaceted role. They are not merely enclosures where animals are observed from a distance, but dynamic institutions at the forefront of conservation and education. Through breeding programs aimed at reviving endangered species, research initiatives that advance our understanding of animal behavior and health, and community outreach that fosters a connection to wildlife, zoos are redefining their purpose in a rapidly changing world.
However, the impact of zoos extends far beyond their gates. They engage millions of visitors each year, nurturing a sense of wonder and responsibility towards the natural world. By presenting compelling narratives about the plight of various species, zoos inspire individuals to become advocates for conservation, emphasizing that every action counts in the fight against habitat loss and climate change.
the relationship between zoos and animal conservation is complex and evolving. While challenges and criticisms accompany this discourse, there is no denying the potential for positive impact that responsible zoos can have on global efforts. As we continue to explore and understand this interplay, it is imperative that we advocate for strategies that maximize effectiveness and ethical considerations alike.
Thus, as we close this examination of zoos’ contributions to animal conservation, let us carry forward the lessons learned, fostering collaboration between scientists, conservationists, and the public. Together, we can build a future where both wildlife and human communities thrive, rekindling hope for generations to come.