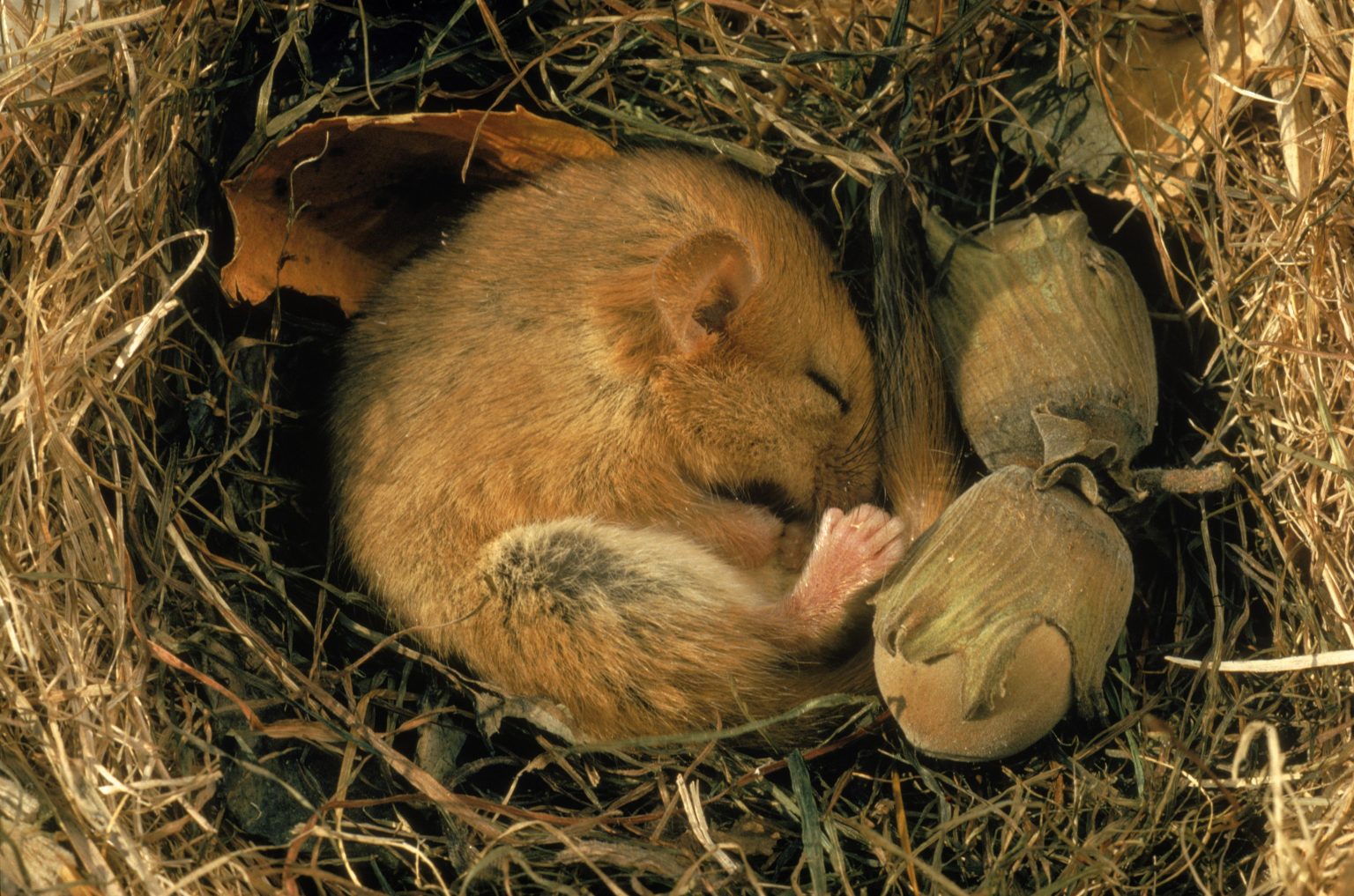
As the chill of winter settles over the landscape, a remarkable phenomenon unfolds in the animal kingdom—hibernation. This extraordinary survival strategy captivates scientists and nature enthusiasts alike, as numerous species retreat into a deep slumber, their metabolic activities slowing to a near standstill. Swirling snowflakes blanket the earth, while beneath the frost, creatures such as bears, bats, and ground squirrels orchestrate a hidden ballet of biology, responding instinctively to the brutal realities of their environment. But what exactly drives these animals to hibernate? What adaptations allow them to endure months of fasting and inactivity? In this article, we embark on a scientific journey to uncover the wonders of animal hibernation. We will explore the intricate processes that underlie this captivating behavior, delve into the evolutionary significance of hibernation, and gain insights into the modern implications of studying these remarkable survival mechanisms in an ever-changing world. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of hibernation and appreciate the resilience of life that thrives, even in the harshest conditions.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Biological Mechanisms of Hibernation in Animals
- The Ecological Importance of Hibernation for Species Survival
- Exploring the Adaptations of Hibernating Animals in Harsh Environments
- Implications for Conservation Efforts and Climate Change Responses
- In Conclusion
Understanding the Biological Mechanisms of Hibernation in Animals
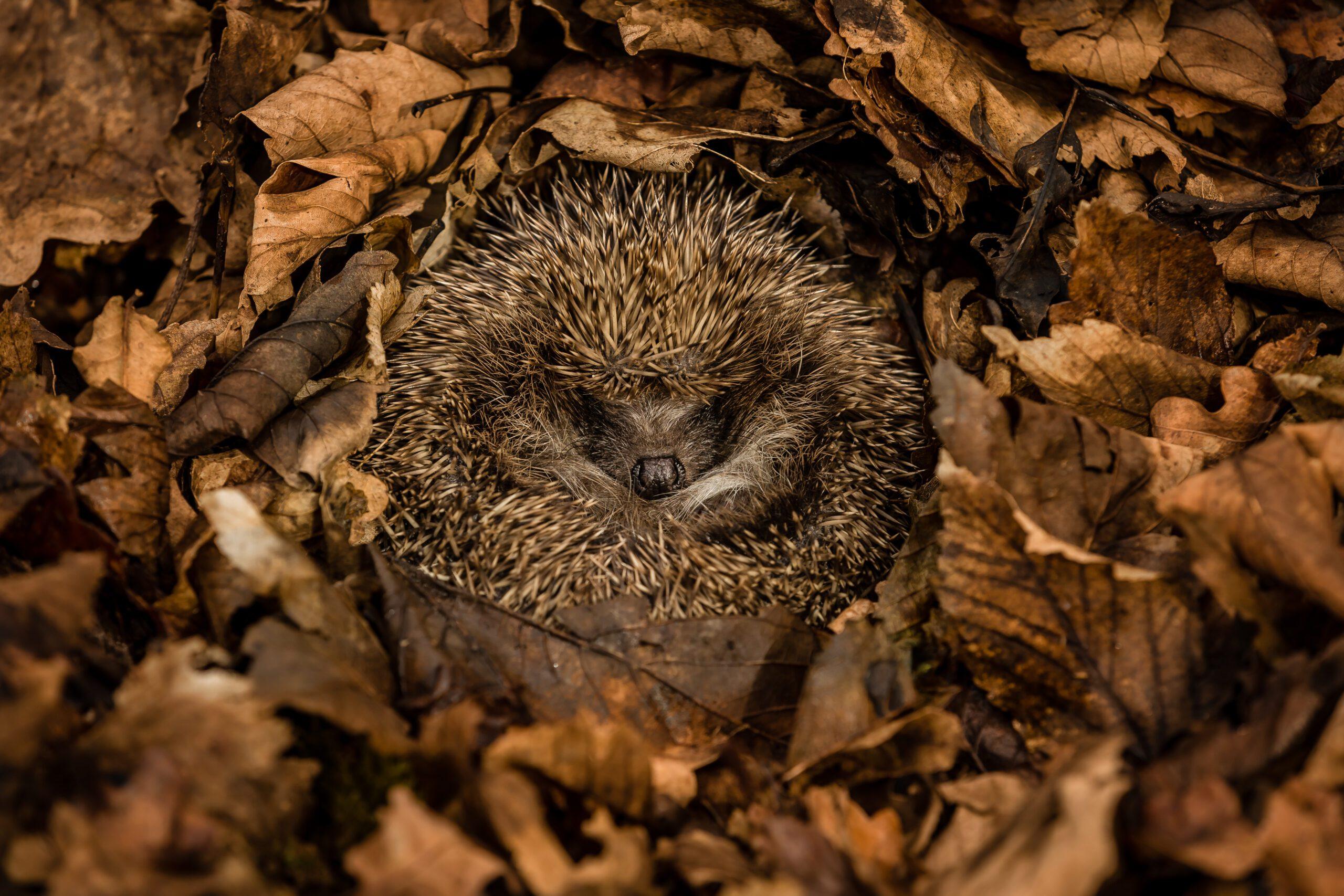

The intriguing phenomenon of hibernation is a complex biological process that allows certain animals to survive harsh environmental conditions. During hibernation, the body undergoes profound physiological changes: heart rates dramatically decrease, metabolic rates plummet, and body temperatures drop significantly. This remarkable adaptation not only enables species like bears, ground squirrels, and bats to conserve energy but also protects them from the dangers of cold weather and food scarcity. The brain plays a critical role in this process, as it triggers the release of hormones that regulate sleep cycles and energy consumption. These hormonal changes serve to ensure that the animal’s body enters a state of dormancy, setting the stage for survival until conditions improve.
Specific biological mechanisms facilitate the hibernation process, showcasing nature’s ingenuity. Key elements include:
- Thermoregulation: Animals can lower their body temperature to conserve energy.
- Metabolic changes: A drastic drop in metabolism allows the animal to survive on stored fats.
- Adaptive brain activity: Some neural pathways modulate sensory input to minimize responsiveness.
Research has led to an understanding of the biochemical pathways involved, such as the role of neuropeptides in signaling sleep states and energy reserves. Laboratory studies have indicated that certain proteins may protect neurons during hypothermia, increasing the likelihood of survival during extreme conditions. Advances in biotechnology may allow scientists to unlock the potential of these hibernation-related mechanisms, potentially influencing human medicine and long-term space travel.
The Ecological Importance of Hibernation for Species Survival

Hibernation serves as a remarkable evolutionary adaptation that allows various species to endure seasonal changes and environmental challenges. As temperatures drop and food sources dwindle, animals that hibernate enter a profound state of dormancy, significantly reducing their metabolic rate. This physiological adjustment enables them to conserve energy and survive without constant foraging. Among the many species that engage in this fascinating process, some noteworthy examples include:
- Black Bears: Rely on fat reserves for sustenance during the winter months.
- Bats: Seek out caves and tree hollows to escape the cold and minimize energy expenditure.
- Ground Squirrels: Dig burrows to create insulated spaces for their hibernation.
This behavioral adaptation not only benefits individual species but also enhances the overall health of ecosystems. By entering hibernation, these creatures help maintain a balanced population level, preventing overgrazing and allowing plant life to regenerate during the growing season. Furthermore, as hibernators emerge in spring, they play a critical role in pollination and seed dispersal, thereby supporting biodiversity. Below is a table outlining some critical ecological roles filled by hibernating species:
| Species | Ecological Role | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Black Bears | Seed Dispersal | Promotes forest regeneration |
| Bats | Insect Control | Reduces pest populations |
| Ground Squirrels | Soil Aeration | Improves nutrient distribution |
Exploring the Adaptations of Hibernating Animals in Harsh Environments
In the icy realms where temperatures plunge and food sources dwindle, certain animal species have honed remarkable adaptations that enable them to survive the harshness of winter through hibernation. This biological process allows animals to significantly lower their metabolic rates, entering a state that conserves energy while they wait for more favorable conditions. Notably, examples can be observed in creatures like the grizzly bear, whose body temperature can drop slightly, permitting them to endure prolonged periods without eating. The intricate design of their hibernation involves various physiological changes, such as reduced heart rate and the production of specific proteins that protect their cells from damage during dormancy.
Moreover, the evolution of hibernation strategies varies among species based on their environments and needs. For instance, small mammals like ground squirrels enter a deep hibernation phase, characterized by complete inactivity, while others may engage in periodic arousals. The table below outlines some fascinating hibernation adaptations across different species:
| Animal | Hibernation Duration | Unique Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Grizzly Bear | Up to 7 months | Lowered metabolism with fat reserves |
| Ground Squirrel | 6-8 months | Periodic arousals to regulate body temperature |
| Wood Frog | Several months | Ability to survive freezing of body tissues |
These adaptations allow each species to respond effectively to environmental challenges, showcasing nature’s ingenuity in the face of adversity. As scientists continue to unravel the intricacies of hibernation, these remarkable phenomena illustrate the delicate balance between survival and the brutal forces of the environment.
Implications for Conservation Efforts and Climate Change Responses
The study of animal hibernation offers profound implications for both conservation efforts and climate change responses. As habitats shift and seasonal patterns become increasingly erratic due to climate change, understanding the mechanisms behind hibernation can inform wildlife management strategies. For instance, identifying species that exhibit strong hibernatory behavior may help conservationists prioritize efforts to protect these animals during critical periods. By focusing on the ecological roles that hibernators play—such as nutrient cycling and population control—conservation programs can be tailored to maintain ecological balance in a changing climate.
Furthermore, the physiological adaptations that enable successful hibernation provide key insights into resilience against climate stressors. As temperatures fluctuate, the ability of certain species to enter a state of dormancy could serve as a model for developing innovative approaches to preserve biodiversity. Highlighted below are some potential strategies:
- Monitoring Hibernation Patterns: Implementing tracking technologies to study hibernation behaviors across various ecosystems.
- Habitat Protection: Designating hibernation habitats as critical zones to mitigate disturbance.
- Research on Hibernation Mechanisms: Collaborating with scientists to explore biochemical processes that could inform medical advancements.
In Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the remarkable phenomenon of animal hibernation, we find ourselves standing at the intersection of biology, survival, and the wonders of nature. The intricate adaptations that allow these creatures to endure the harshest seasons provide us not only with insight into their lives but also with a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of ecosystems. Through the lens of science, we have uncovered how mammals, reptiles, and amphibians navigate their world’s rhythms, transforming adversity into an incredible evolutionary strategy.
Yet, as we marvel at these natural wonders, we must also acknowledge the challenges facing many hibernating species in our rapidly changing environment. Climate change, habitat loss, and human encroachment pose threats that can disrupt these ancient patterns of survival, reminding us of the intricate connections between species and the ecosystems they inhabit.
As we move forward, let us carry with us the knowledge garnered from this scientific journey—an understanding that enriches not only our appreciation of wildlife but also our responsibility to protect it. The mysteries of hibernation remind us of nature’s resilience and fragility, urging us to be vigilant stewards of the world we share. By fostering a deeper connection to the natural world, we can contribute to a future where these wonders continue to thrive, season after season.