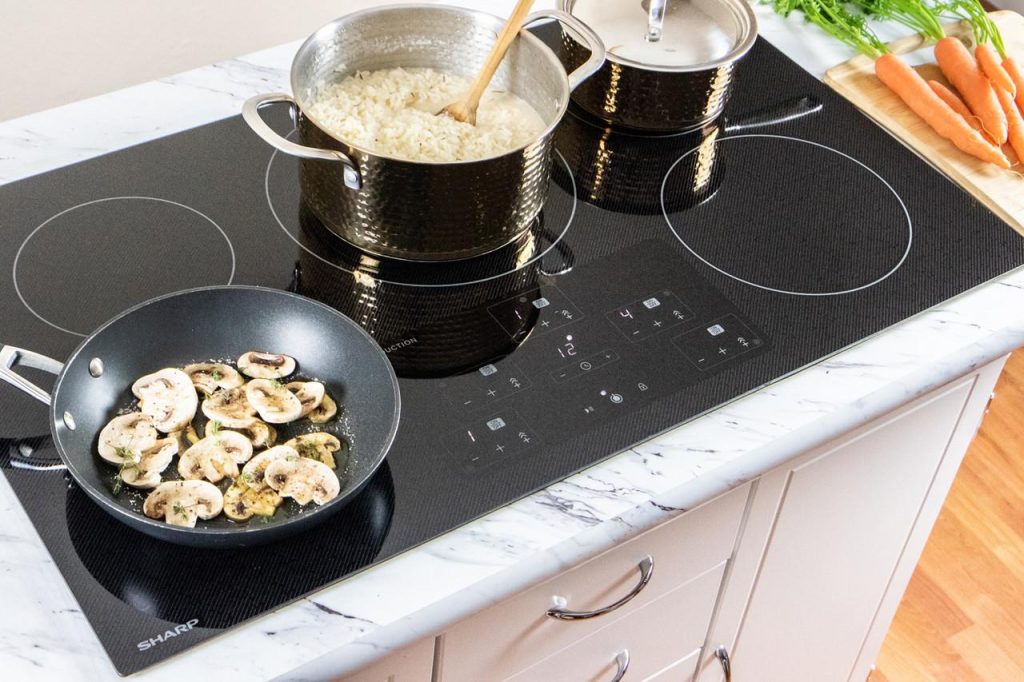
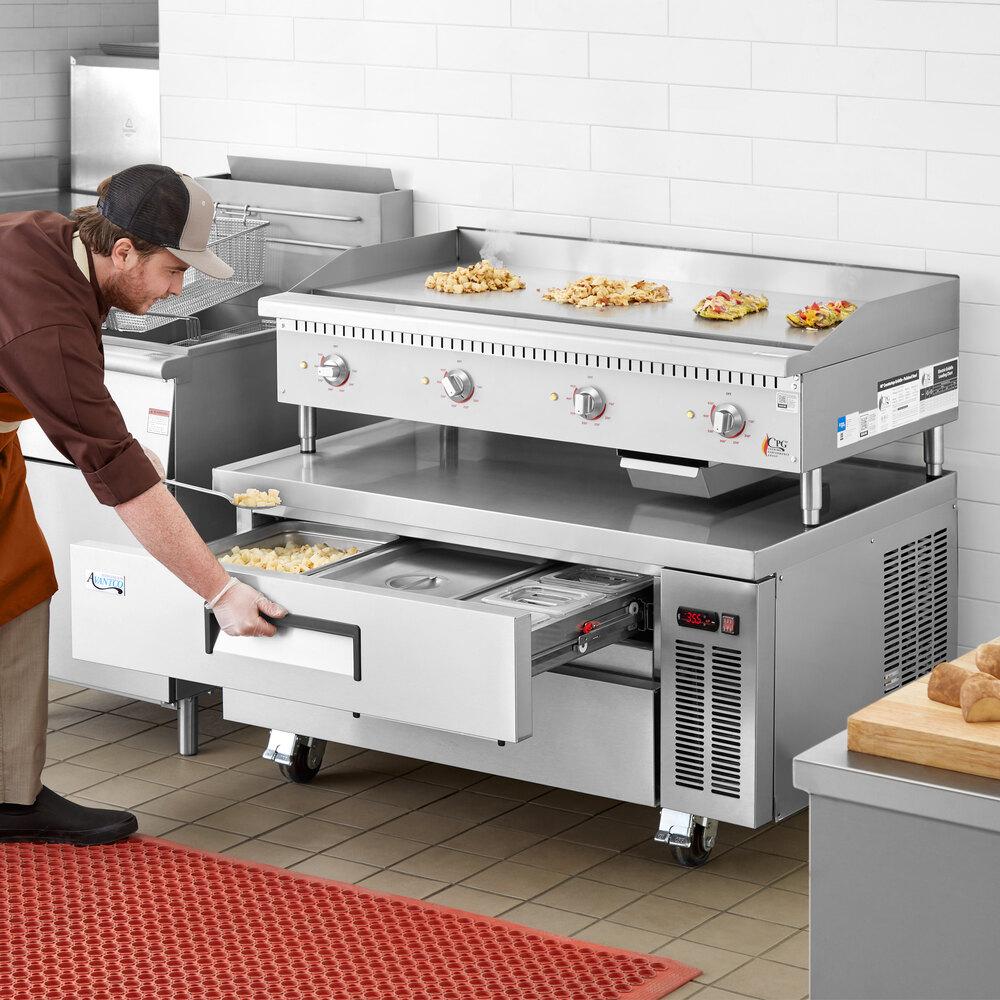
In the realm of modern kitchens, the choice of a cooking stove serves as a pivotal decision for both amateur chefs and seasoned culinary professionals. Among the myriad options available, induction and gas stoves stand out as two of the most popular choices, each boasting unique features and benefits. Induction stoves, known for their sleek design and rapid heating capabilities, utilize electromagnetism to heat pots and pans directly, offering a level of efficiency and safety that has captured the attention of many homeowners. On the other hand, gas stoves, with their time-honored tradition and immediate flame control, are celebrated for their reliability and versatility in diverse cooking techniques. Yet, with such contrasting advantages, the debate over which stove reigns supreme continues to simmer. In this article, we will delve into the pros and cons of induction and gas stoves, providing a comprehensive overview that aims to illuminate the best choice for your culinary needs.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Efficiency and Energy Consumption of Induction and Gas Stoves
- Evaluating Cooking Performance and Heat Control for Culinary Enthusiasts
- Analyzing Cost Implications and Long-Term Value for Induction and Gas Options
- Assessing Safety Features and User Experiences in Everyday Cooking Scenarios
- Concluding Remarks
Understanding the Efficiency and Energy Consumption of Induction and Gas Stoves

When evaluating the efficiency and energy consumption of induction and gas stoves, it is crucial to consider their respective heating technologies. Induction stoves, which use electromagnetic energy to directly heat cookware, tend to be more energy-efficient. They can convert about 90% of the energy they consume into heat, meaning that a significant portion of the power used directly contributes to cooking. In contrast, gas stoves typically convert only 40-60% of their energy into heat, as much of it dissipates into the surrounding environment. This not only affects cooking times but also translates into higher energy costs over time.
In terms of energy consumption, the differences become even more pronounced when examining cooking efficiency. Induction cooktops not only heat up faster than their gas counterparts but also allow for precise temperature control. Some key points to consider include:
- Heat-up time: Induction stoves can boil water in as little as 2 minutes, while gas may take several more minutes.
- Cookware requirements: Induction cooking requires magnetic cookware, whereas gas works with all types of pots and pans.
- Safety and ease of use: Induction stoves cool down quickly, reducing the risk of burns, while gas burners require careful monitoring of open flames.
These factors collectively influence not only the cooking experience but also long-term energy consumption and costs, making it essential to weigh these aspects when choosing between induction and gas stoves.
Evaluating Cooking Performance and Heat Control for Culinary Enthusiasts

When it comes to culinary performance, the debate between induction and gas stoves is a lively one among cooking enthusiasts. Induction stoves utilize electromagnetic fields to heat pots and pans directly, allowing for immediate temperature adjustments. This precise control over heat can significantly enhance cooking techniques, making tasks like searing meat or melting chocolate much easier. Additionally, the surface of an induction stove remains cool to the touch during cooking, which can lead to a safer cooking environment, especially in busy kitchens. However, one downside is that induction cooking requires ferrous cookware, and some chefs may feel limited by the need to invest in new pots and pans.
In contrast, gas stoves offer a visual indicator of heat levels through the flame, providing an intuitive experience for cooks who prefer to gauge temperature with their eyes. The ability to adjust heat instantly with knobs can be particularly advantageous for recipes requiring precise simmering or rapid boiling. Furthermore, gas cooking provides a unique flavor experience, especially for techniques like charring or flambéing, that some chefs feel cannot be replicated on an induction cooktop. However, gas stoves can lead to uneven heating in certain cookware, and the open flame can pose safety concerns. Below is a comparison to summarize key features of both cooking methods:
| Feature | Induction Stoves | Gas Stoves |
|---|---|---|
| Efficacy | High efficiency due to direct heating | Moderate efficiency with heat loss |
| Heat Control | Precise & instant | Visual & adjustable |
| Safety | Cool surface; less risk of burns | Open flame; higher burn risk |
| Cookware Compatibility | Requires specific materials | Works with most cookware |
| Flavor Enhancement | Less direct flavor impact | Enhanced charring & flavor |
Analyzing Cost Implications and Long-Term Value for Induction and Gas Options
When considering the cost implications of induction versus gas stoves, several factors come into play that could influence your decision. Upfront investment is one of the most significant aspects. Induction stoves typically have a higher initial cost, ranging from $1,000 to $3,000 for quality models, compared to gas stoves that can start as low as $500. However, induction cooking is generally more energy-efficient, often leading to lower utility bills over time. Furthermore, the rapid heating and adjustable temperature settings of induction cooktops can minimize energy waste, translating into potential long-term savings.
Beyond initial expenses, it’s crucial to evaluate maintenance and repairs when determining long-term value. Induction stoves have fewer mechanical components and do not require gas lines, which can lower repair costs and the risk of gas leaks. Furthermore, induction units are easier to clean due to their smooth surfaces, potentially saving time and cleaning product expenses. On the other hand, gas stoves might incur additional expenses related to ventilation systems or gas supply, which can add up over the years. A concise comparison of these factors is illustrated in the table below:
| Aspect | Induction Stoves | Gas Stoves |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | High ($1,000 – $3,000) | Moderate ($500+) |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Low | Varied |
| Cleaning Ease | Easy | Moderate |
Assessing Safety Features and User Experiences in Everyday Cooking Scenarios
When evaluating the safety features of induction and gas stoves, it’s essential to recognize the distinct characteristics that make each one unique. Induction stoves rely on magnetic fields to heat cookware directly, which minimizes the risk of burns since the cooktop surface remains cooler during cooking. Notably, many induction models come equipped with safety shutoff features that automatically turn the stove off when no cookware is detected. On the other hand, gas stoves utilize an open flame, presenting a higher risk of fire hazards or accidental burns. However, modern gas stoves often include flame failure devices that shut off the gas supply if the flame goes out, providing an additional layer of safety to address this concern.
User experiences with both cooking methods reveal notable preferences influenced by safety and usability. Users of induction stoves appreciate the speed at which they heat up and cool down, facilitating quick adjustments and reducing the risk of overcooking. Additional user-friendly aspects include precise temperature control and easy cleanup since spills are less likely to burn onto the surface. Conversely, gas stove enthusiasts value the immediate visual feedback of the flame, which can enhance cooking precision, particularly for techniques like sautéing or searing. Although gas stoves may require more vigilance regarding safety practices, many home cooks find the sensory experience of cooking with flame to be irreplaceable, balancing their passion for cooking with essential safety measures. The following table outlines user experiences and safety assessments for each stove type:
| Feature | Induction Stoves | Gas Stoves |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Control | Precise | Visual Feedback |
| Burn Hazard | Low | Moderate |
| Spill Cleanup | Easy | Moderate |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
Concluding Remarks
the choice between induction and gas stoves ultimately hinges on individual cooking preferences, lifestyle, and priorities. Induction stoves, with their rapid heating capabilities and energy efficiency, offer a modern approach that appeals to those seeking precision and safety in the kitchen. Their sleek designs and easy cleanup contribute to a streamlined cooking experience. On the other hand, gas stoves retain a strong following due to their reliability, distinctive flame control, and the tactile experience they provide for traditionalists and culinary enthusiasts alike.
As outlined in this comparison, each option presents its own distinct advantages and limitations. Those who value speed and efficiency may lean towards induction, while others who find comfort in the familiarity of gas may resist the change. Ultimately, the decision rests on what matters most to each cook: the allure of cutting-edge technology or the satisfying embrace of classic culinary practices. By understanding the nuanced strengths and weaknesses of both types of stoves, consumers can make an informed choice that best suits their cooking style and kitchen needs. Whatever path you choose, the right stove can enhance not only your culinary creations but also your overall kitchen experience.